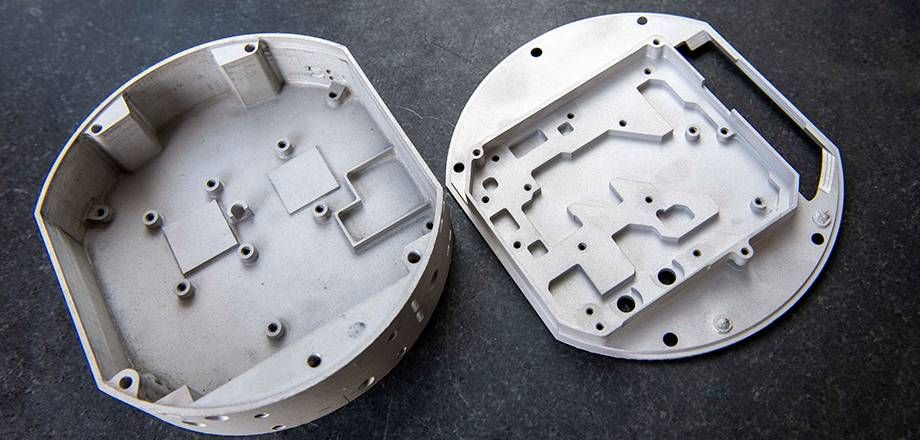
The manufacturing process known as mold making involves creating various parts using a flexible material against a rigid form known as a mold or matrix. The molds themselves can be made from materials such as steel, aluminium, and even wood, while the materials filling the mold cavity can include glass, amorphous metals, plastics, fiberglass resin, or rubber.
Aluminium alloys are versatile, cost-effective, and widely used as a material for mold making. At Anıl Makina, we have experience and a skilled team in the manufacturing of aluminium injection and plastic injection molds, producing molds with great precision to meet your specific needs.
Aluminium Alloys in Mold Making
Different aluminium alloy plates that are effective in mold production should be selected based on the specific application. When determining the right aluminium alloy for your mold application, considerations such as part geometry, resin type used, cycle time, quantity, and the durability of the finished product should be taken into account. Some popular alloys used in mold creation include:
- 7075-T651 plate aluminium alloy provides excellent strength.
- 7050 aluminium alloy is widely used for blow molds, structural foam molds, and injection molds. These molds are limited to a thickness of 8 inches or less.
- 6061-T651 plate aluminium alloy is used in large blow molds, compression molds, and low-volume injection molds.
- 6013 aluminium alloy provides superior strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability with good machinability and hardness levels. It can be relied upon for producing a range of batch sizes, from a few hundred to several thousand.
- 2024 aluminium alloy is used for blow or structural foam molding and is reliable for short production runs.
- M-1 mold plate is an exceptional, high-strength aluminium plate specifically designed and developed for the plastic and mold industries. It offers exceptional density, dimensional stability, and strength, along with advantages in machinability to reduce production costs.
- MAX 5 aluminium mold plate is a great option for larger rubber and plastic mold applications.
Design Considerations in Molding
Designing plastic parts for plastic mold manufacturing is a complex task that involves multiple factors. Questions such as "How will the part be used?" "How does it fit with other parts in assembly?" and "What types of loads will it encounter in service?" come into play. In addition to functional and structural considerations, processing issues play a significant role in the design of an injection-molded plastic part. The way molten plastic enters, fills, and cools in the cavity greatly influences the form the part will take.
Following some basic rules of injection-molded part design will result in easier manufacturing, assembly, and typically a much stronger part in service. Breaking down a part into basic groups minimizes molding issues and helps you logically build your part. Always keep in mind how the part will be molded and what you can do to minimize stress.
Standard Mold Making with CNC Machining
Traditional standard machining involves the manual use of lathes, milling machines, and drill presses. With advanced technology, CNC machining has become the dominant method for creating more complex and precise molds while utilizing standard machining techniques.
In modern CNC systems, both mold design and manufacturing processes are highly automated. The mechanical dimensions of the mold are defined using computer-aided design (CAD) software and then transformed into manufacturing instructions using computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. The "post-processor" software then converts these instructions into specific commands required for each machine used in mold creation. These commands are loaded into the CNC machine, and the manufacturing process begins.
